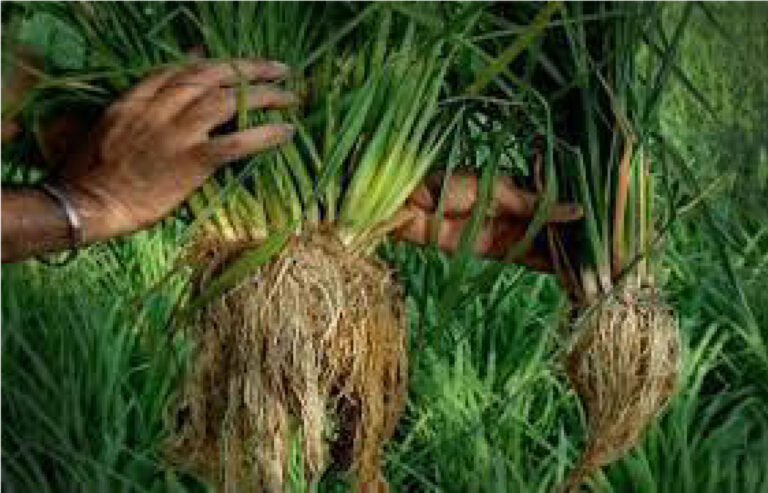
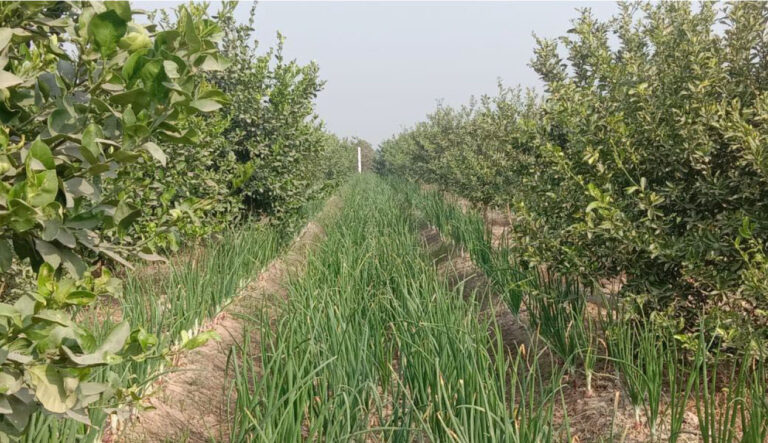
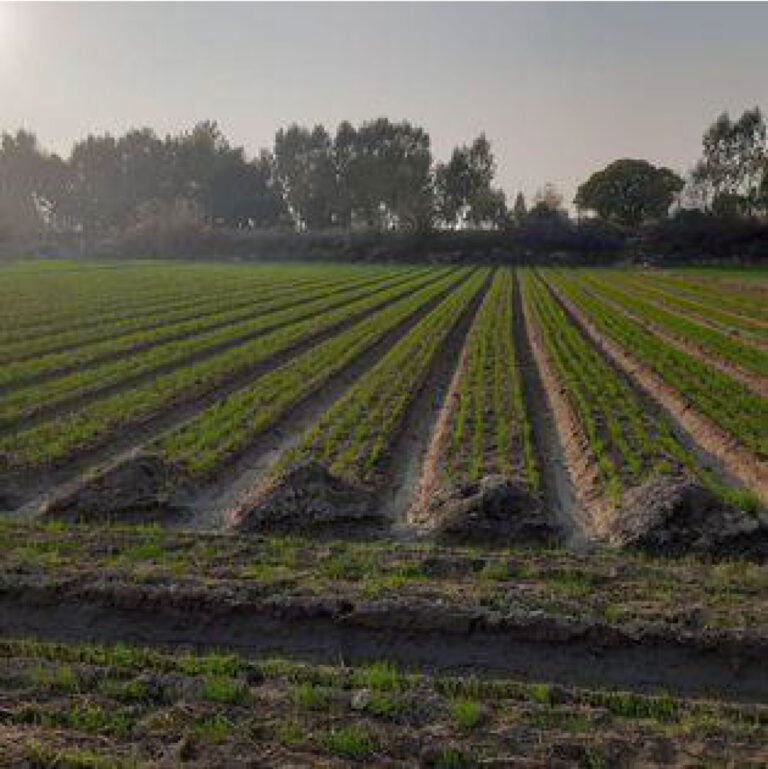
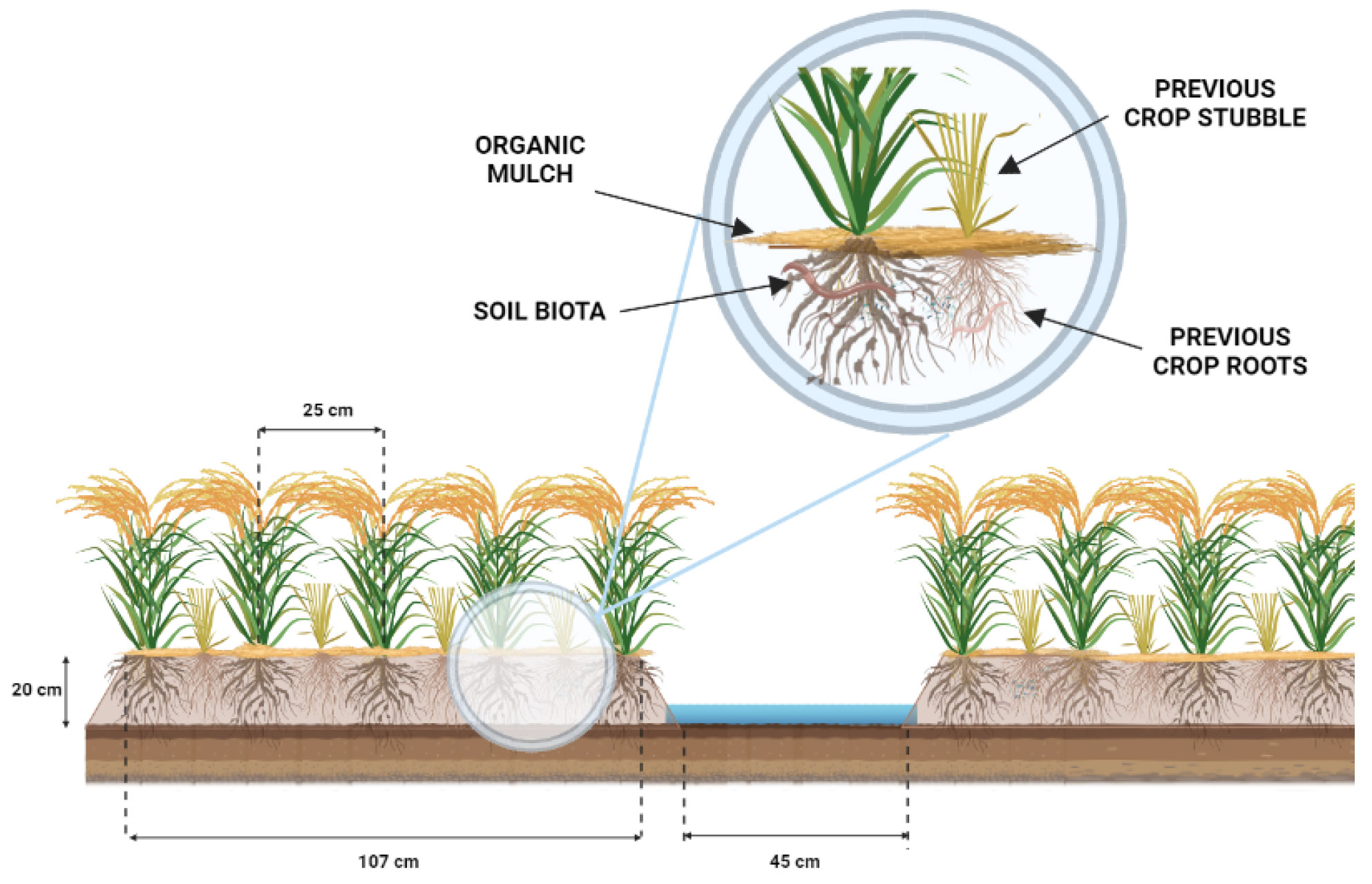
Under PQNK, crops are cultivated on permanent no-till raised beds that are formed on levelled, non-compacted land. For this, the beds’ size is adapted to the size of the tractor and machinery wheels, so that the wheels are driving through the furrows, hence not compacting the beds. Beds are covered with organic mulch that can be locally procured by leaving crop residues on the field after harvesting and by using cover crops in between cash crops. Irrigation is applied in the furrows between beds. Nutrient uptake from the soil is optimised by plant spacing and hardpan breaking. The plant spacing also allows each plant to develop large canopies for catching sunlight and CO2 from the atmosphere. The plant spacing is to be adapted to the specific requirement of each crop. Under PQNK, crop establishment can be done by both transplanting or direct seeding. Direct planting is preferable, but if choosing to transplant the seedlings, one should do this early and carefully to bring minimal disturbance to the root systems. Intercropping, relay cropping, and under-sowing are techniques that can be used by farmers practising PQNK to promote crop diversification within the farming system. Introducing agroforestry practices such as alley cropping, where trees are placed within the agricultural field, is also a way to increase the available in-field biomass for mulching and to promote biodiversity while increasing farm production.